Virtual reality (VR) was once a concept relegated to science fiction, but today, it’s at the forefront of innovation across various industries. From gaming and education to healthcare and beyond, VR is transforming how we learn, work, and interact with the world around us. But what exactly is virtual reality, and how is it shaping the future?
This blog dives into the fascinating world of VR, its current applications, and the potential it holds for the future. Whether you’re a VR enthusiast, a curious newcomer, or a professional exploring its use for business, this post has something for you.
What Is Virtual Reality?
At its core, virtual reality is a computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional environment that users can interact with. Unlike traditional two-dimensional media like a movie or video game on a screen, VR immerses the user in a fully interactive 360-degree environment using a VR headset.
There are two main types of VR experiences widely available today:
- Immersive VR – Uses VR headsets to create a completely virtual environment where users feel fully “present.” This is often used for gaming, training simulations, or virtual tours.
- Augmented Reality (AR) – Combines virtual elements with the physical world, often through apps or AR glasses. While not full VR, AR enhances reality with digital overlays.
Now that we know what VR is, let’s explore how it’s bringing innovation to different sectors.
The Current Applications of Virtual Reality
Virtual reality is no longer just about gaming. Its versatility allows it to thrive across various industries. Here’s how VR is making an impact today:
1. Gaming and Entertainment
Gaming is perhaps the most well-known application of VR. Platforms like the Oculus Quest and PlayStation VR allow users to immerse themselves in lifelike video game worlds. From exploring alien planets to participating in thrilling escape rooms, VR gaming offers unmatched interactivity and adrenaline-pumping experiences.
Entertainment industries are also starting to integrate VR. For example, immersive films and concerts allow audiences to “step into” the action. Live sports can now be experienced in VR to get front-row seats—without actually being in the stadium.
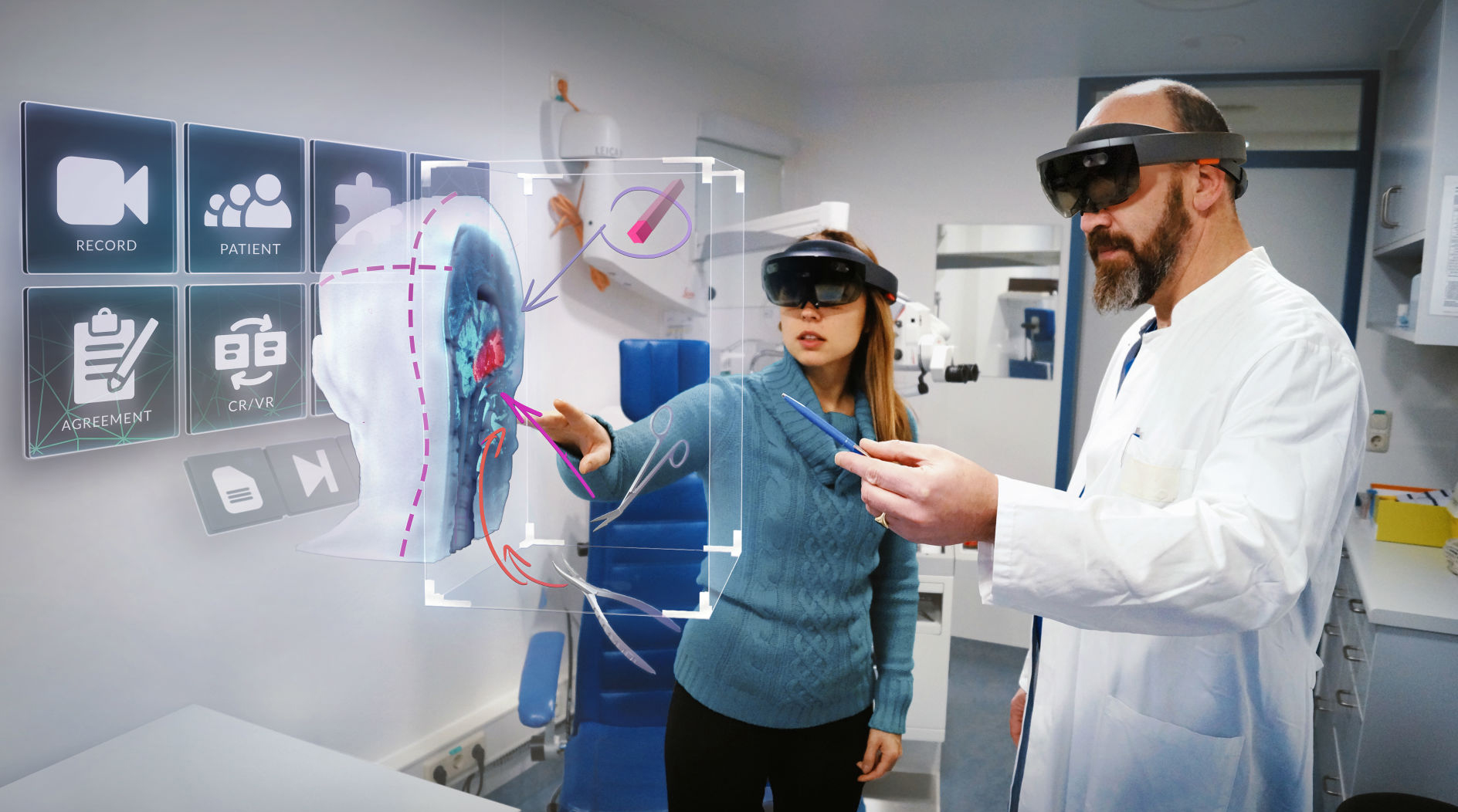
2. Healthcare
The adoption of VR in healthcare is remarkably promising. VR is revolutionizing patient diagnosis, treatment, and education. Some uses include:
- Training for Surgeons – Medical students and surgeons use VR simulations to practice highly technical surgeries without any risk to patients.
- Therapy and Mental Health – VR therapy has shown success in treating PTSD, social anxiety, and phobias by immersing patients in controlled environments for gradual exposure.
- Pain Management – Patients can use VR to shift focus away from pain during medical treatments or rehabilitation.
Studies have found VR effective in increasing patient engagement while improving overall outcomes.
3. Education and Training
VR takes “learning by doing” to new heights. By immersing learners in simulated environments, it allows them to practice skills that would otherwise be inaccessible.
- Classroom Learning – Students can explore ancient ruins or outer space without leaving their desks.
- Corporate Training – Companies like Walmart and Boeing use VR to train employees in retail processes and airplane maintenance. VR ensures hands-on experience without operational risks.
This technology turns passive learning into active participation, making it ideal for both schools and businesses.
4. Real Estate
The real estate industry benefits greatly from VR’s visual and interactive capabilities.
- Virtual Property Tours – Buyers and renters can “walk through” homes from the comfort of their own devices.
- Staging Made Easy – Real estate agents can digitally stage empty homes in VR to help buyers visualize the possibilities.
VR streamlines the buying process, saving time for agents and clients alike.
5. Retail and E-commerce
How do you improve online shopping? By making it interactive, just like a store visit.
- VR platforms allow customers to virtually try on clothes, explore furniture layouts in their own home, or assess the finishing details of a car before buying.
- Retailers can track engagement and customize recommendations in real time for an ultra-personalized shopping experience.
Brands like IKEA and Sephora are already capitalizing on VR to build stronger customer connections.
6. Team Collaboration and Remote Work
The rise of remote work has increased demand for better tools to stay connected. Enter VR platforms like Spatial and VR Chat, which simulate office spaces for teams scattered across the globe.
- Teams can meet “almost in-person” to brainstorm, collaborate, and present ideas in immersive 3D settings.
- Training sessions seem more realistic and engaging as employees interact in shared virtual spaces.
VR is reshaping how businesses operate and flourish in the remote working era.
The Future of Virtual Reality
While VR has made significant advances, we’ve only scratched the surface of its potential. Here’s what the future could hold.
Enhanced Accessibility
The cost of VR hardware, like headsets, has been a barrier for mass adoption. However, advancements in technology are expected to make VR more affordable, compact, and lightweight. This will open the doors for broader use in homes, schools, and workplaces.
Expanding VR into Everyday Life
VR will likely become a part of our daily routines, enhancing every experience:
- Shopping in fully virtual malls.
- Traveling to “virtual vacations” with lifelike simulations.
- Socializing through lifelike avatars in digital spaces.
Integration With AI
The combination of VR and artificial intelligence (AI) will make experiences smarter and more personalized. Imagine virtual instructors who adapt based on your learning style or virtual travel guides who customize tours to your preferences.
Exploring the Metaverse
The much-talked-about metaverse is set to amplify VR adoption. A fully immersive digital environment, the metaverse would allow users to work, socialize, and shop virtually. While still in its infancy, this concept has the potential to redefine entire sectors.
Can Your Business Leverage VR?
Virtual reality is no longer a trend—it’s a tool that drives innovation, engagement, and efficiency. Whether you’re managing a small business or leading a large enterprise, there’s an opportunity for you to integrate VR into your operations.
VR technology continues to inspire and push the boundaries of innovation. Are you ready to be part of the VR revolution?
FAQs About Virtual Reality
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual reality is a technology that allows users to experience and interact with a computer-generated, three-dimensional environment. By using VR headsets and controllers, users can immerse themselves in these environments, making activities like gaming, training, and virtual meetings feel real.
How is VR used in businesses?
Businesses use VR for a variety of applications, including employee training, product design, virtual tours, marketing, and customer engagement. For example, companies can simulate challenging work scenarios for employee skill development or create immersive customer experiences through virtual showrooms.
Do I need expensive equipment to use VR?
While high-end VR headsets and systems can be costly, there are affordable options available on the market. Devices like standalone VR headsets or even smartphone-based VR can serve as entry points, depending on your specific needs and goals.
Is VR suitable for small businesses?
Absolutely. VR is scalable and can be tailored to suit small businesses seeking innovative solutions to engage with customers, improve training programs, or stand out in competitive markets. Many affordable VR tools are designed with smaller operations in mind.
What are the challenges of adopting VR?
Some common challenges include the initial cost of hardware and software, ensuring staff are properly trained to use the technology, and keeping up with ongoing updates in VR advancements. However, strategic planning and gradual implementation can help overcome these hurdles.